In a recent article, we laid out the benefits of a programmatic approach to pentesting.
To briefly recap: a pentest program is a series of pentests conducted over a defined period to systematically find and fix vulnerabilities in one or more assets. Programs usually run on a rolling annual basis, with tests completed at predetermined intervals — e.g., monthly or quarterly.
This approach ensures:
-
Continual testing coverage for critical and frequently updated assets; and,
-
A much higher likelihood that high-risk vulnerabilities will be found and fixed promptly.
Breaking Down the Steps of the Pentest Program Lifecycle
While the specifics vary, the underlying structure of a pentest program follows seven simple steps:
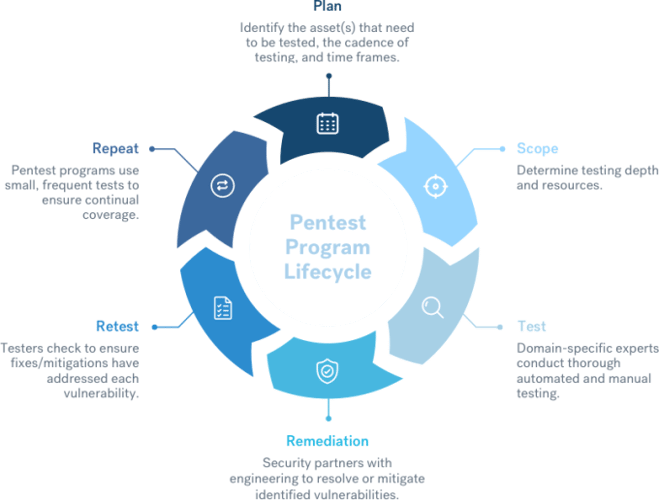
Step #1: Plan
The first step in establishing a pentest program is to plan out your program and set objectives. This includes determining which assets will be in scope, how regularly testing will take place, and what time frame the program will span.
Many organizations overlook the importance of setting clear objectives, instead seeing pentesting as simply a ‘must have’ for their security program. In reality, the objectives you set could completely change the way your program is structured.
For instance, depending on whether your primary objective is compliance or security, you could end up including different assets and working with a totally different testing schedule.
Step #2: Scope
Once your basic plan is in place, it’s time to determine what format the testing will take. This includes making a decision on which security testing partner you’ll work with, and how exactly the testing will be structured.
For instance, a pentest program could primarily use:
-
White box pentesting — Pentesters have full access to source code, architectural diagrams, and in-depth details. Source code is the key here, not just fully informed of the function or design of the assets.
-
Grey box pentesting — Pentesters have access to the asset that may include elevated privileges and have some understanding of the asset’s internal workings.
-
Black box pentesting — Testers are given no information, context, or privileged access to assets.
While there are arguments in favor of black box testing, gray, and white box testing usually provide superior results.
Note: A common mistake is to include too many assets in a pentest program, so testers don’t have enough time to test thoroughly. If you aren’t sure, ask your pentest provider for guidance.
Step #3: Test
This stage usually begins with the customer meeting the testing team. At Cobalt, we assign testers to match the needs of each program, ensuring the team includes relevant domain-specific expertise. We then start with a 30-minute call to introduce their customer to their team and set up a Slack channel to allow direct communication throughout the program.
With the preparatory steps out of the way, it’s time for testing to begin.
The team conducts thorough testing using a mixture of automated and manual techniques. If the program is white or gray box, there is often an ongoing discussion between the customer and the testing team to ensure maximum testing coverage and depth.
Step #4: Remediation
Although we’ve listed this as a separate step, vulnerability reporting and remediation is really an ongoing process that runs throughout the testing window. The customer receives a report of each vulnerability as soon as it’s identified and triaged, enabling them to start working on fixes immediately.
Once the testing window is complete, the customer receives a final report of all findings.
Step #5: Retest
Once the customer has applied a fix for a vulnerability, it is promptly retested to ensure the fix is effective. At Cobalt, customers simply mark findings as ‘Ready for Retest’ on our platform. The fix is then verified by the testing team lead, and the customer’s report is updated.
As a pentest program progresses, it’s common for lessons to be learned about what works, what doesn’t, and what could be done better. Both customers and testers often have feedback that can be used to improve future tests, and these lessons are shared after each pentest.
Step #7: Repeat
This is the most critical stage of all, and what really distinguishes pentest programs from traditional pentests. In a pentest program, testing is completed at predetermined intervals on an ongoing basis, ensuring maximum testing coverage and minimizing cyber risk.
How To Build a Comprehensive Pentest Program
If you’re considering starting a pentest program, there are several things you should know. To guide you through the process, we’ve created the Comprehensive Guide to Building a Pentest Program.
Download the guide today to learn:
-
What a pentest program is (and isn’t), and what makes it different to other testing delivery models.
-
The benefits of a programmatic approach to security testing compared to one-off penetration tests.
-
A full rundown on building a pentest program, from setting objectives to incremental improvement.
-
Who should be involved in your pentest program, and how to win the support of executives.
-
How we built our own pentest program and Cobalt, and what lessons we’ve learned along the way.
-
Why pentest programs outperform traditional testing for incremental cyber risk reduction.
Download a free guide on building a pentest program orexplore Cobalt's PtaaS Platform directly.










